We knew it wouldn’t be long before Google released their first core update of...

10 Advantages of Writing Custom Structured Data
10 Advantages of Writing Custom Structured Data
When it comes to bespoke structured data, there’s nothing better than being able to do it yourself!
In this blog, Kelly Sheppard, Senior Technical SEO Lead and resident structured data writer here at Sleeping Giant Media, explores 10 reasons why custom structured data is the best.
As the saying goes, if you want something done properly, you’ve to do it yourself. Relying on plugins such as Yoast to write your structured data means that you are restricting your site to the most basic types – and may not be getting the results you truly deserve. And if you’re going to the effort of thinking about structured data, you want to be seeing results.
Let’s dive into 10 reasons why custom structured data is absolutely worth investing in.
1.Flexibility
When we’re in control, we can tailor the structured data we write to the exact length and specificity we need for a site – which helps us align with a business’s priorities and product features. Plugins, however, can’t do this – as they are often restricted to certain types of content.
Just look at the difference between entities here. The image below shows entities from automatically generated structured data:
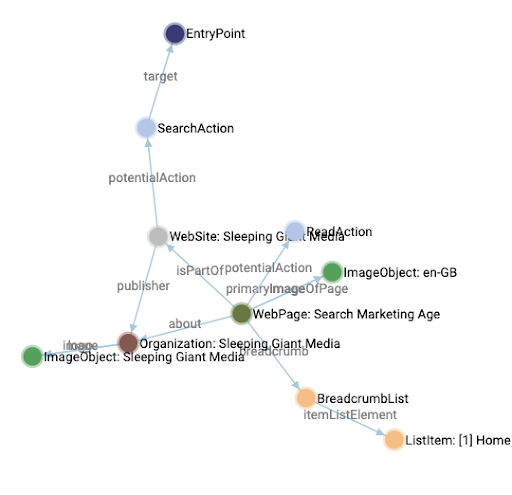
Whereas the screenshot below shows the entities from the same page, but where the structured data was written by us:
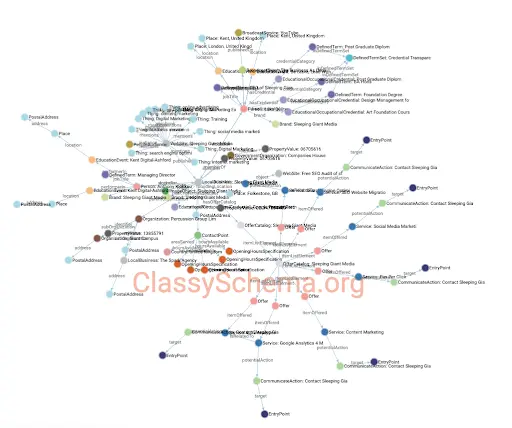
2.Schema types
Did you know that there are over 800 different types of schema? By writing custom-based structured data, we can use as many as we want to (within reason – and obviously making sure they don’t conflict). Plugins are normally restricted to one or two types per page, and only around 20 different schema types overall. A significant difference.
3.Accuracy
When creating, we check our schema with 3 different testers to make sure that it conforms to both Google standards and Schema.org standards. We also visualise all of the entity connections, in order to make sure they all line up and are related to each other correctly.
As you can see below, structured data created by plugins often has errors or warnings.
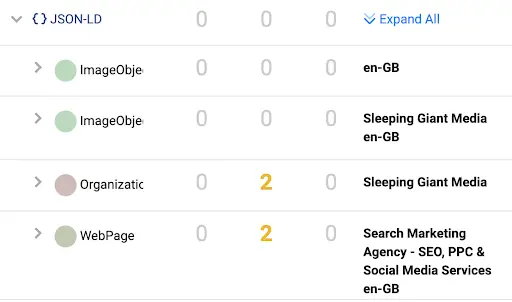
4. Control
When we’re the writers, we have complete control over how we nest the structured data together with the other types on a site. Creating these connections can often be tricky, but by doing it manually, we can make sure they are the best possible ones to use. This means we also have complete control over how we connect the entities on a site too.

5. Uniqueness
When it comes to Sleeping Giant Media, our structured data offering is unique. In fact, we’d go as far as to say that we don’t know of any other digital marketing agency in the UK that can write structured data like us!
Automatically generated structured data from plugins is all the same – with the same connectors, same schema types and same features. This is why bespoke schema can really help you really stand out from your competitors.
6. The strength of connectors
There are some connectors which are stronger than others. When writing, we can make sure that we use the strongest connectors for the best entities on a page – meaning that search engines will consider these pages stronger for that entity than other less relevant pages. Plugins can’t do this, as they don’t understand the entities and the relationships between them.
7. Unique information
Using structured data in this way means the website will really stand out from the crowd – as well as standing out to search engines. You can provide unique and relevant information that search engine bots otherwise wouldn’t necessarily know about by marking up the pages with special structured data types and fields. All of this can help Google and other search engines understand your content better, and even index your site more quickly!
8. Results!
We know that around 58% of users click on Rich Results1 in SERPs. Structured data can help you show up in the search results for things like product results, review stars, featured snippets, tables, images and much more!
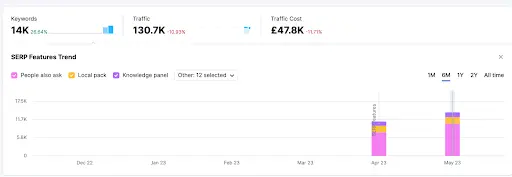
We added structured data to 34/8,200 pages on the website relating to the screenshot above, and in just 2 months they are showing rich results for 14,000 keywords – which bring in 130,000 clicks a month.
9. E-E-A-T
By strengthening your brand identity through entity based SEO, we can help the E-E-A-T (expertise, experience, authority, and trust) on your website, as Google will have more of an idea of what you offer and how those products or services connect with your brand. We can also add reviews, awards and more information about the people who work for you. All of these things help increase your brand visibility and overall E-E-A-T value.
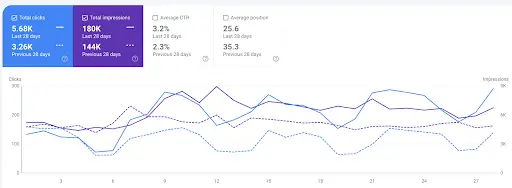
We added custom structured data to two pages on this customer’s website – the homepage and ‘About’ page. In just 2 weeks, clicks increased by +74% and impressions by +25%, as we increased their EEAT and they started appearing for various rich results regarding the topic of dementia – even outranking the NHS in some circumstances!
10. Entity based structured data
I saved the best reason until last. Plugins can’t yet write entity based structured data – whereas we can!
Using knowledge bases such as Wikipedia and Wikidata, we can let search engines know exactly what your content is about, meaning less ambiguity around those entities and how they relate to each other, your business and your products.
When doing a page by page strategy and entity SEO process, we need the structured data to strengthen and bond all those things together. In our case, our Content Team writes fantastic entity-based content, the technical SEO for the page is sorted, but we need the final piece to pull it all together. This is where the entity-based structured data supports the content on the page and tells Google what it’s all about.
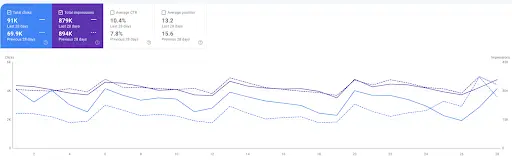
In the image above, we updated this client’s structured data on their homepage to entity based structured data. This is the traffic generated just by adding entities to the page, so Google actually understands more about what the content and website is about. That’s a +30% increase in clicks and -1.6% decrease in impressions (meaning traffic is more relevant). The average CTR and position have also increased. This is the last 28 days compared to the previous 28 days.
So, to recap – writing custom structured data is important. Why?
Custom structured data can help search engines:
- Understand your content better
- Index your site more quickly
- Improve your E-E-A-T
- Boost click through rate
- Aid brand visibility
- Reduce uncertainty around entities
- Create new connections between brands, products and services
- Find out new information about entities it otherwise might not know about
Want to know more, or want some help with creating structured data for your site? Reach out to the whizzkids on our dedicated SEO team – they’ve got all of your structured data needs covered. And, to learn more about entities, technical SEO, and structured data, keep up with our blog.
Sources:
1 https://blog.milestoneinternet.com/seo/seo-click-curves-get-58-clicks-per-100/
Blog
Giant Wednesday
How To Optimise Images For Websites
Digital Marketing, technology & business insights, how-to's and explainer...
Follow Us
Sign Up For More
Stay up to date with the latest happenings, learnings, events & more with our GIANT Newsletters.
Contact Us
Top Floor, The Civic Centre, Castle Hill Avenue, Folkestone CT20 2QY.